- Which material is used for gaskets?
- Why are Gasket Material Types Important For Gasoline?
- Different Gasket Material Types
- Key Factors When Selecting Gasket Material Types
- Gasket material types FAQs
- Learn more about MEGA Gasket Material Types
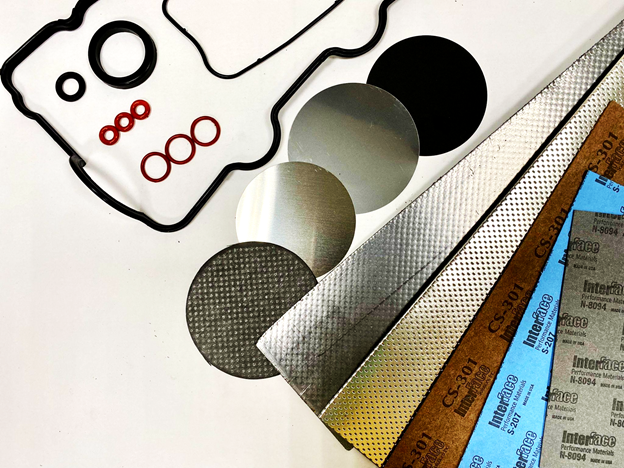
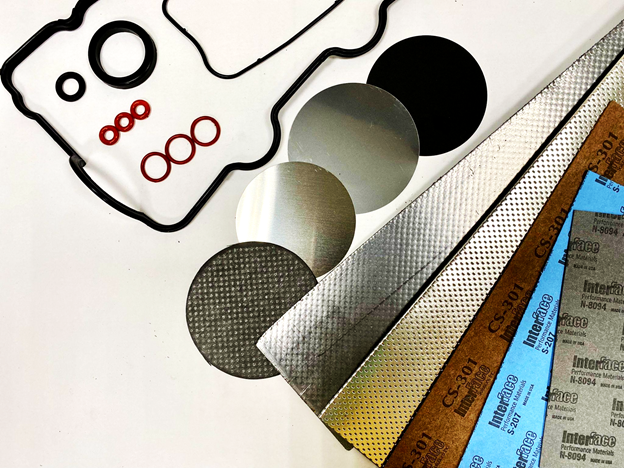
Gaskets are crucial components in different pieces of equipment. They provide a mechanical seal, ensuring that fluids do not leak into other areas, causing contamination. Since they are a critical part of various systems it is important to choose the right type of gasket during the production process. In particular, manufacturers must select a gasket that is made from the right material.
Which material is used for gaskets?
The gasket material is made from will alter how it operates for a specific application. There are various materials used for producing gaskets. Common gasket materials include rubber, graphite, metal, asbestos free, and more. This makes it more difficult to choose the right option. Below, we’ll discuss some of the key considerations that you should keep in mind when choosing a gasket material for gasoline fluid process equipment.
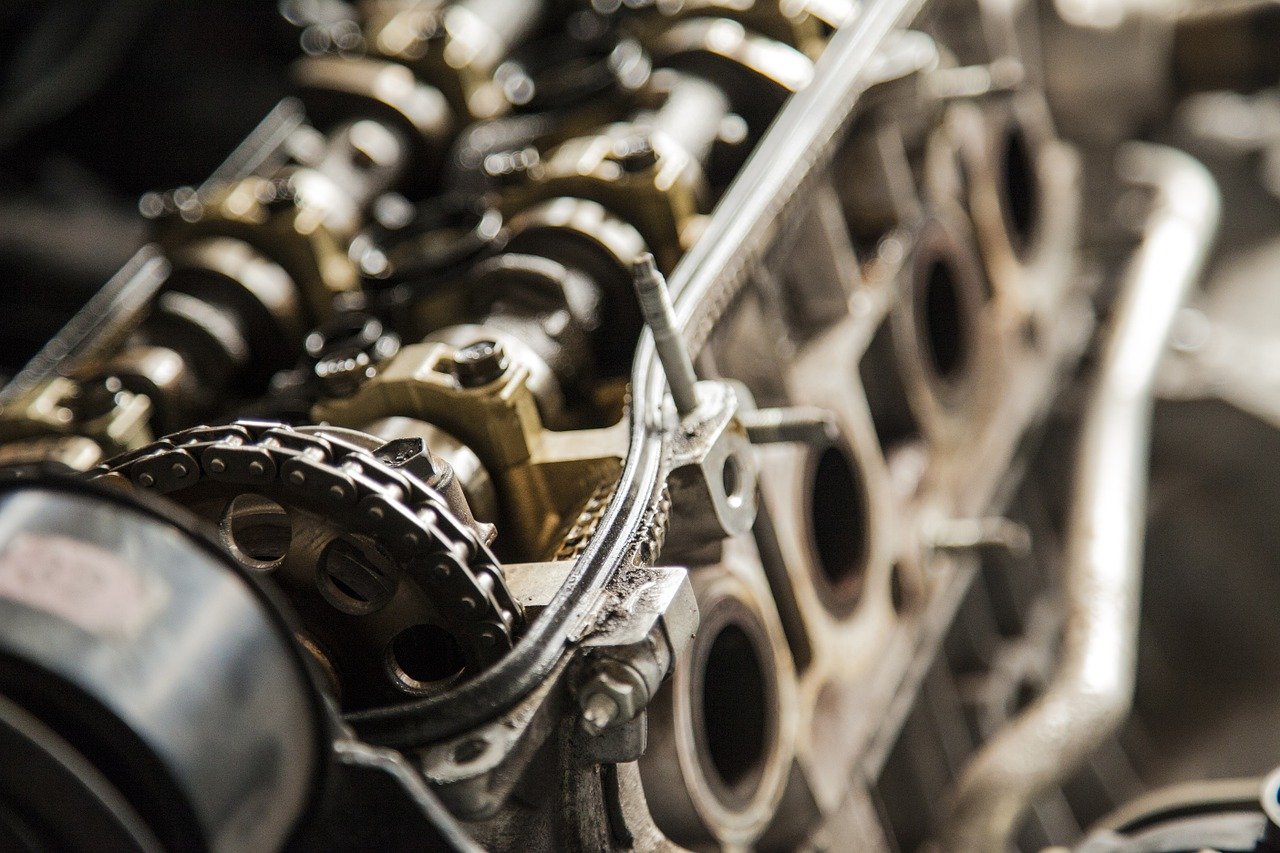
Why are Gasket Material Types Important For Gasoline?
There are thousands of engineered materials specifically produced by production companies. Despite the massive selection of materials, no one material will fit the requirements of all applications.
Gasket material cakages not being an issue
Gaskets provide a cushioning, sealing material between two parts of a piece of equipment to ensure that leakages do not become an issue. Every machine that uses gasoline requires gaskets to ensure that they work correctly. This includes hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical equipment regardless of the size of the material.
Right gasket material types can provide safety for the machinery
Gasket material types are important for gasoline because they must correspond directly with a specific use or requirement. For instance, the gasket material used for an internal combustion engine needs to be compatible with fuel system components including fuel injectors.
If the wrong gasket material type is chosen then this could mean that a piece of equipment does not work correctly. A potential gasoline leak could even result in machinery being unsafe. If gasoline leaks through joins, it may cause a fire hazard.
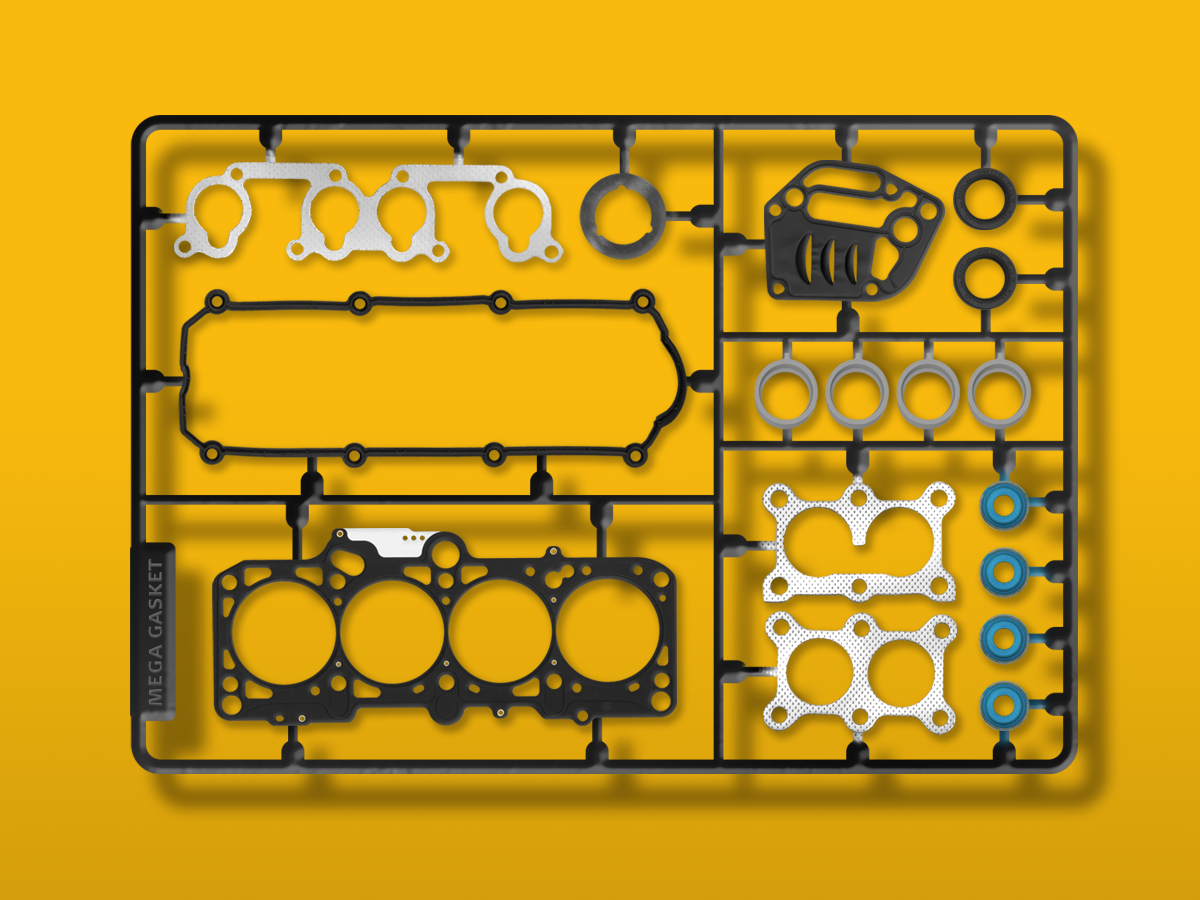
Different Gasket Material Types
There are various different gasket materials that may be suitable for use in the automotive industry as well as for other applications. These are some of the options that can be considered as well as their unique characteristics that could mean they are the correct choice for a specific application.
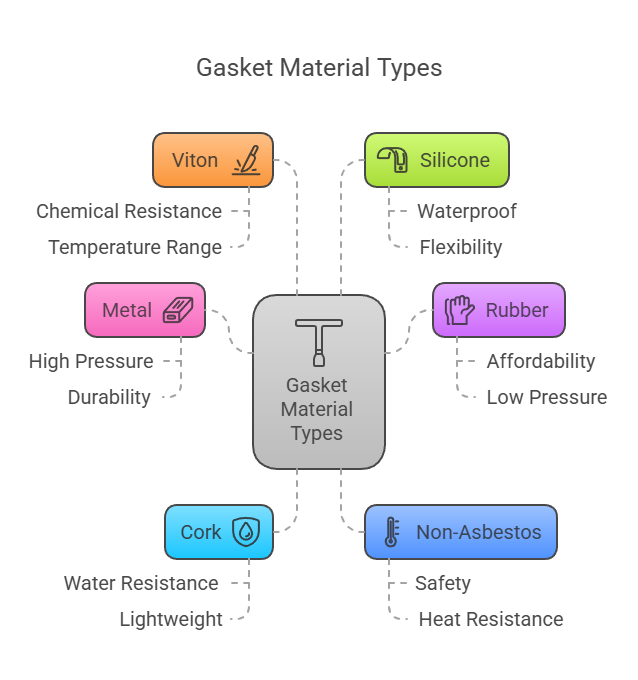
Metal
Metal gaskets are ideal for high-pressure applications. A metallic gasket will provide a line contact or alternatively may contain the fluid through the use of wedging after the flush connection surfaces touch. These gaskets may also be referred to as ring gaskets. They tend to have an octagonal or cross section.
Some metallic gaskets can handle pressure up to 20,000 psi. Due to this, metal gaskets are commonly used in gasoline and oil industrial systems. They are typically secured with high-tension bolting.
Some of the most common materials for metallic gaskets include monel, stainless steel, low carbon steel, and Inconel.
More about MEGA metal gasket material: Metal/Steel Gasket Selection
Rubber
Rubber is one example of a non-metallic or soft gasket. They provide compression between two surfaces with low levels of pressure or tension. They can be used in applications where the fluid contents have low levels of pressure themselves and as such can not force a pathway through the gasket. A key benefit of non-metallic soft materials such as rubber is that they are affordable. They can also be used for low-temperature applications. However, certain materials that are non-metal such as graphite can be used in high-temperature systems up to 500 degrees celsius.
More about Graphite gasket: Graphite Gasket: The Material, Temperature Range, And More
Cork Gasket Materials
Cork gasket materials are lightweight and very stable. They also have the ability to resist water penetration and provide a high level of compressibility as well as a strong resistance to oil with no lateral flow. A key benefit of using cork is that it will remain durable and is resistant to issues with wear.
Cork may also be combined with rubber to create a synthetic material that can be used to provide both flexibility and resilience. This can help provide a stronger defense against different weather conditions as well as environmental issues such as fungus and acid.
Non-Asbestos
Non-asbestos gasket materials (asbestos free gasket) replaced asbestos gaskets following the 1990’s ban on toxic materials. Previous to this ban, asbestos gaskets were commonly used for heavy industrial applications as well as for engines. Asbestos was used for gaskets due to its fantastic level of heat resistance. As well as providing resistance to higher temperatures, non-asbestos gaskets are also resistant to different chemicals and provide a high level of joint stability.
Today modern non-asbestos gaskets are created from materials such as aramid fibers that are blended with polymers. These are designed for use with high-temperature applications.
Viton
Gaskets can be made from Viton. This is a brand of fluoropolymer elastomer and rubber. It is suited for both harsh environments as well as high temperatures. A commercial grade material, Viton will also withstand harsh chemicals as well as cold environments and is commonly used for gaskets that will be used in OEM. The temperature range of Viton is between -20°C and 205°C. This depends on the grade of the material. It can withstand lower temperatures such as -30°C. However, this will only be the case for short working periods.
Silicone
Gaskets may also be made from silicone in the form of sponge and foam or even as a solid. Silicone gaskets are 100% waterproof and as such will not degrade over time due to water exposure. They are also flexible which means that they won’t sustain damage at high temperatures. The material won’t shrink either however it is not suitable for steam or hydrocarbon applications.
Key Factors When Selecting Gasket Material Types
Selecting the right gasket material is crucial to ensure proper sealing, durability, and system performance. Below are the key factors you should consider:
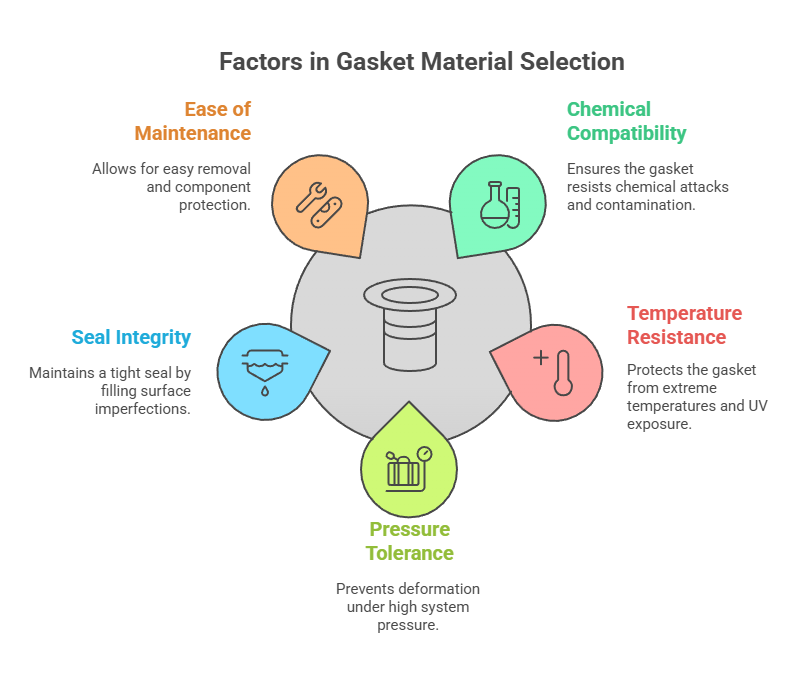
Chemical Compatibility
The gasket material must be compatible with the substance it is sealing — such as gasoline, coolant, or oil. It should resist chemical attacks and must not contaminate the medium. Gases are particularly difficult to seal compared to liquids, and some chemicals become more aggressive at higher temperatures.
Temperature Resistance
Gaskets operate in environments ranging from freezing temperatures to internal heat exceeding 140°C, especially under the hood or in direct sunlight. The material should also resist damage from UV rays and ozone exposure. Materials like silicone offer greater resilience under such conditions.
Pressure Tolerance
High system pressure can deform gaskets and joints. That's why gasket materials are rated with a P × T (Pressure × Temperature) value. Always check the rating to ensure the material can withstand the operating conditions of your system.
Seal Integrity and Compressibility
An effective gasket material must compress enough to fill surface imperfections and form a tight seal. It should also be non-porous to prevent leakage of gas or fluid and maintain sealing under varying thermal or mechanical stress.
Ease of Removal and Maintenance
For maintenance or repairs, the gasket material should allow easy removal without leaving residue or damaging components. This ensures efficient part replacement and reduces downtime during service.
Gasket material types FAQs
What is the most commonly used gasket material?
The most commonly used gaskets are rubber, metal, and graphite. Rubber gaskets are versatile and chemically resistant, suitable for many applications. Metal gaskets are durable and ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature environments. Graphite gaskets excel in extreme conditions, resisting high temperatures and chemicals, making them essential in industries like oil and petrochemicals. These three types cover a wide range of sealing needs.
1. Which material is used for gaskets?
Gaskets are made from a wide range of materials to suit different applications. Common materials include rubber (e.g., silicone, EPDM, or neoprene), metal (e.g., stainless steel, copper), and non-metallic materials (e.g., graphite, cork, or PTFE). Each material is selected based on factors like temperature resistance, pressure handling, and chemical compatibility.
2. What is the three 3 categories of gasket?
Gaskets are typically categorized into three main types:
- Non-metallic gaskets: Made from materials like rubber, cork, or graphite, ideal for low-pressure and low-temperature applications.
- Metallic gaskets: Composed of metals such as stainless steel, used in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
- Composite gaskets: A combination of metal and non-metallic materials, providing enhanced sealing for challenging conditions.
3. What is standard gasket material?
The standard gasket material varies depending on the application, but compressed fiber sheets, graphite, and rubber materials are commonly used for general industrial purposes. PTFE is often used for chemical resistance, while metallic gaskets like stainless steel are standard in high-pressure environments.
Learn more about MEGA Gasket Material Types
We hope this helps you understand some of the key considerations when choosing gasket materials. If you need more assistance or are keen to order gaskets please do not hesitate to contact MEGA Gaskets using our web page. One of our friendly experts will respond to your query without delay.
 |
Author: MEGA Gasket established since 1979, granted ISO 9002 in 1999 and updated to ISO 9001:2015 in 2017, and the main production is for automobile and all kind of engine gaskets. MEGA have profuse experience and good reputation in Taiwan. Learn more about MEGA Gasket manufacturer and supplier. |